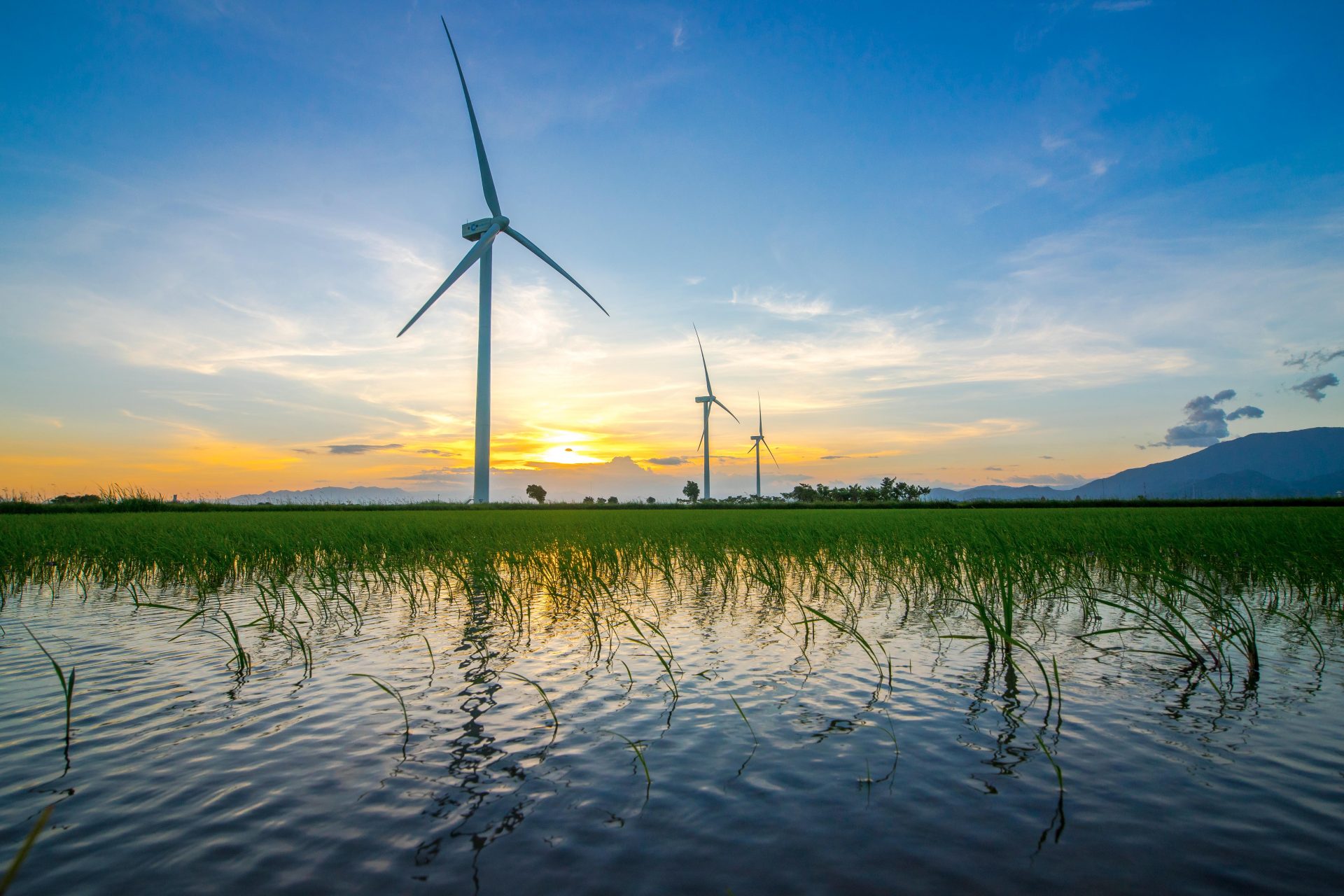
Water is the foundation of successful mitigation action: Earth's climate system and water cycle are deeply intertwined.

Part I. Setting the Scene on Freshwater’s Role in Mitigation: A Physical Science and Governance Background
The report starts with providing a background and context by introducing the biophysical interdependencies of freshwater’s role for climate mitigation, and the governance context of climate mitigation measures.
Read more about Part IChapter 2. Freshwater’s role for climate mitigation – the physical science basis
Chapter 2 focuses on the intricate relationship between climate and water in the larger context of the Earth system. It explains how climate mitigation measures fundamentally depend on, and impact, freshwater resources and the water cycle and why a functioning freshwater cycle is crucial for climate mitigation measures to reach their full potential.
Chapter 3. Governance context of mitigation measures
Chapter 3 provides an overview of the global governance frameworks and national instruments relating to climate change, biodiversity, land, water, and sustainable development. It also covers various financing mechanisms and instruments available to realise the goals outlined in these frameworks. The review points out the existing barriers to achieve climate mitigation as leverage points are not capitalised on, and risks are not accounted for. It also highlights that integrated approaches are needed to overcome these barriers.

Part II: Water-related mitigation opportunities across biomes and sectors
The second part provides an analysis of climate mitigation measures, keying in on their use of, and impacts on, freshwater and freshwater-dependent systems.
Read more about Part IIChapter 4. Mitigation measures in drinking-water and sanitation services
Chapter 4 examines the mitigation potential and risks in drinking water and wastewater management. It includes abstraction, treatment, distribution and discharge, and accounting for both direct and indirect GHG emissions including the electricity consumption associated with indirect carbon emissions. Lowering the release of these GHGs presents major opportunities for climate change mitigation.
Chapter 5. Mitigation measures in freshwater ecosystems
Chapter 5 examines mitigation potential and risks in freshwater ecosystems. Aquatic environments, such as freshwater peatlands, marshes, swamps, lakes, streams, rivers, and tidal wetlands, can function as either GHG sources or sinks, depending on their use and the climate. To account for the emission reduction services from freshwater systems, it is necessary to include them as part of a portfolio of measures to reduce GHG emissions.
Chapter 6. Mitigation measures in land systems
Chapter 6 examines mitigation potential and risks in land systems. Mitigation measures in land systems can have notable synergies but also trade-offs with local-to-regional water sustainability goals. Land system mitigation measures have the potential to decrease soil erosion, increase groundwater recharge, and increase water vapour exchange with the atmosphere, thereby enhancing local cooling and regional rainfall. Misguided implementation of land system mitigation measures can, on the other hand, cause local water shortage, biodiversity loss, and harm to local communities.
Chapter 7. Mitigation measures in energy system
Chapter 7 examines the water-related climate mitigation potential and risks of low-emission energy transition plans. To enable the transition to renewable energies, strategies are also needed to mitigate potential water risks for energy storage solutions, including pumped hydropower, as well as mining for minerals. Low emission energy scenarios often lack quantification of impacts on water quality and ecosystems, which must be incorporated in national, local and regional planning.

Part III: Integrating freshwater into climate change mitigation planning and action
The third part draws cross-sectoral conclusions building on the findings in Part II, identifying priority risks and opportunities for water-wise climate planning, including ‘win-wins’.
Read more about Part IIIChapter 8. Water-mitigation leverage points and risk hotspots globally
Chapter 8 presents priority water risks that need to be evaluated in climate mitigation plans. Building on Part II, this chapter outlines opportunities to effectively mitigate emissions through measures taken in water and sanitation services and the protection, restoration and management of ecosystems. The chapter also touches upon key issues for climate mitigation that are beyond the scope of this report, including industrial processes and design, transport, solid waste management, as well as issues related to diet, sustainable consumption and behavioural change.
Chapter 9. Achieving climate mitigation through integrated and cross-sectoral approaches
Chapter 9 demonstrates the need for integrated approaches to achieve water-wise climate mitigation. This chapter provides an overview of some of these approaches, including Integrated Water Resources Management (IWRM), the Water-Energy-Food Nexus approach, Source-to-Sea (S2S), the Landscape approach, and Integrated Urban Management, each exemplified through case studies.
For our governance systems and national implementation plans to succeed we need to place water in its rightful place: at the heart of all efforts to adapt to, as well as to mitigate climate change.
Key Messages: Unpacking Freshwater’s Role in Climate Change Mitigation
- Climate mitigation measures depend on freshwater resources. Present and future freshwater availability needs to be accounted for in climate mitigation planning and action.
- Climate mitigation measures impact freshwater. Freshwater impacts – both positive and negative – need to be evaluated and included in climate mitigation planning and action.
- Water and sanitation management can reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Climate mitigation planning and action should include the substantial emission reduction potential in drinking water and sanitation services and through the management and protection of freshwater resources.
- Nature-based solutions to mitigate climate change can deliver multiple benefits for people and the environment. Priority should be given to measures that can safeguard freshwater resources, protect biodiversity, and ensure sustainable and resilient livelihoods.
- Joint water and climate governance need to be coordinated and strengthened. Mainstreaming freshwater in all climate mitigation planning and action requires polycentric and inclusive governance arrangements that can facilitate integrated approaches.
Pre-launch at the Bonn Climate Change Conference
The Executive Summary was initially presented at the Unpacking freshwater’s role in climate change mitigation Side Event at the SB56 UN Climate Change Conference in Bonn, Germany, on June 13 2022.
Watch the recording of the Side Event:
We need to act now!
Limiting global warming to 1.5 degree is still narrowly within reach, and water across terrestrial, aquatic, and technological systems plays a critical role for the necessary transformation towards net-zero.
Read the full Executive Summary
This report has been made possible thanks to the collaboration of our partners



This report is funded by




